Eino ADK: Workflow Agent
WorkflowAgent 支持以静态的模式运行多个 Agent。所谓“静态”,是指 Agent 之间的协作流程(如顺序、并行)是在代码中预先定义好的,而不是在运行时由 Agent 动态决定的。Eino ADK 提供了三种基础 Workflow Agent:Sequential、Parallel、Loop,他们之间可以互相嵌套以完成更复杂的任务。
默认情况下,Workflow 中每个 Agent 的输入由 History 章节中介绍的方式生成,可以通过 WithHistoryRewriter 自定 AgentInput 生成方式。
当 Agent 产生 ExitAction Event 后,Workflow Agent 会立刻退出,无论之后有没有其他需要运行的 Agent。
SequentialAgent
SequentialAgent 会按照你提供的顺序,依次执行一系列 Agent:
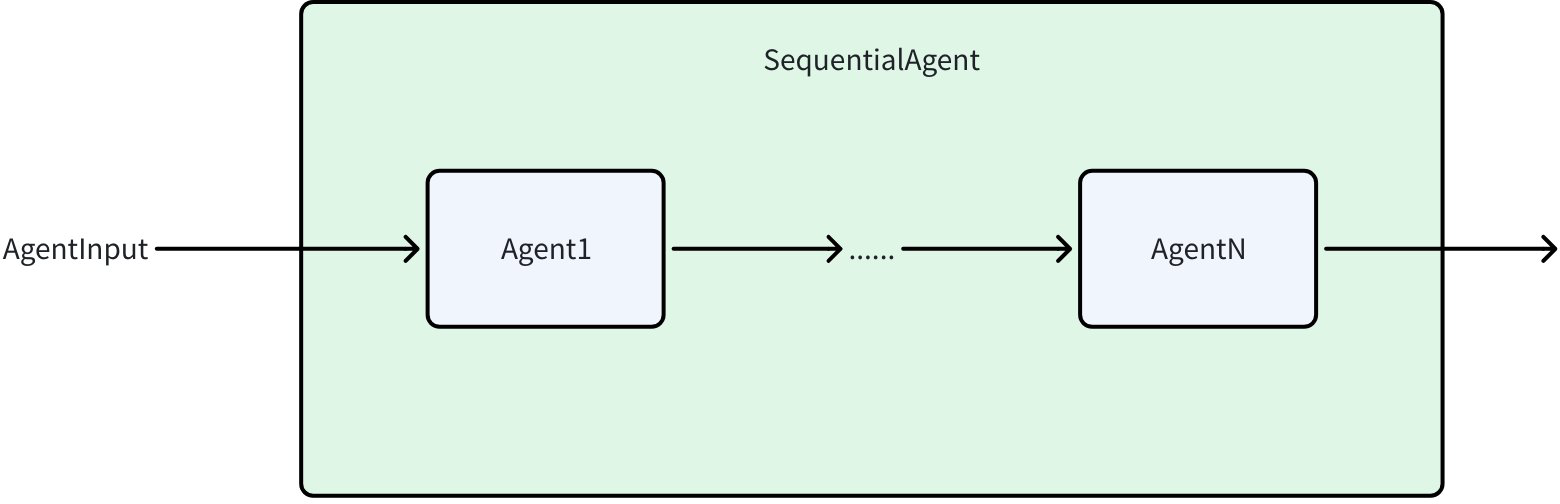
我们通过一个包含两个子 Agent 的 Research Agent 来介绍 SequentialAgent 的用法,其中第一个 Plan Agent 会接收一个研究主题,并生成研究计划;第二个 Write Agent 会接收研究主题与 Plan 产生研究计划(Write Agent 的输入依据 History 章节中介绍的默认方式生成,也可以通过 WithHistoryRewriter 自定义),并撰写报告。
首先创建两个子 Agent ,我们将两个 Agent 简化为仅包含 ChatModel,实践中可以通过为 Agent 增加 Tool 来增强 Agent 的 plan 和 write 能力:
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
)
func newChatModel() model.ToolCallingChatModel {
cm, err := openai.NewChatModel(context.Background(), &openai.ChatModelConfig{
APIKey: os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
Model: os.Getenv("OPENAI_MODEL"),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return cm
}
func NewPlanAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "PlannerAgent",
Description: "Generates a research plan based on a topic.",
Instruction: `
You are an expert research planner.
Your goal is to create a comprehensive, step-by-step research plan for a given topic.
The plan should be logical, clear, and easy to follow.
The user will provide the research topic. Your output must ONLY be the research plan itself, without any conversational text, introductions, or summaries.`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
func NewWriterAgent() adk.Agent {
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(context.Background(), &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "WriterAgent",
Description: "Writes a report based on a research plan.",
Instruction: `
You are an expert academic writer.
You will be provided with a detailed research plan.
Your task is to expand on this plan to write a comprehensive, well-structured, and in-depth report.
The user will provide the research plan. Your output should be the complete final report.`,
Model: newChatModel(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return a
}
之后使用 Sequential Agent 编排两个子 Agent:
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples/adk/intro/workflow/sequential/subagents"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
a, err := adk.NewSequentialAgent(ctx, &adk.SequentialAgentConfig{
Name: "ResearchAgent",
Description: "A sequential workflow for planning and writing a research report.",
SubAgents: []adk.Agent{subagents.NewPlanAgent(), subagents.NewWriterAgent()},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{
Agent: a,
})
iter := runner.Query(ctx, "The history of Large Language Models")
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error: %v\n", event.Err)
break
}
msg, err := event.Output.MessageOutput.GetMessage()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Agent[%s]:\n %+v\n\n===========\n\n", event.AgentName, msg)
}
}
运行结果如下:
Agent[PlannerAgent]:
assistant: Step 1: Define the Research Scope
- Determine the time frame for your historical analysis, starting from the early development of large language models (LLMs) to the present.
......
Step 10: Update and Revise
- Plan for periodic updates to incorporate new developments in large language models as they arise.
- Keep abreast of publications and ongoing research in the field to maintain the relevance and accuracy of your research.
finish_reason: stop
usage: &{86 675 761}
===========
Agent[WriterAgent]:
assistant: # The History of Large Language Models
## Introduction
The development of Large Language Models (LLMs) marks a significant milestone in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP). These models, capable of understanding and generating human-like text, have evolved rapidly over the past few decades, showcasing profound improvements in language comprehension and generation. This report explores the history of LLMs, tracing their evolution from early linguistic theories to the sophisticated models we see today.
## Early Foundations in Linguistics and Computation
......
## Conclusion
The history of Large Language Models is a testament to the rapid evolution of artificial intelligence. From early linguistic theories and basic neural networks to sophisticated models capable of human-like language generation, each milestone has contributed to our current understanding and capabilities. As LLMs continue to advance, their potential to transform industries, improve communication, and enable new technologies remains vast. However, it is crucial that ethical considerations keep pace with technological advances to ensure these models benefit society at large.
---
This comprehensive overview of the history of Large Language Models outlines their origins, evolution, and impact, providing a foundation for further exploration and research in this dynamic field.
finish_reason: stop
usage: &{74 1066 1140}
===========
LoopAgent
LoopAgent 基于 SequentialAgent 实现,在 SequentialAgent 运行完成后,再次从头运行:
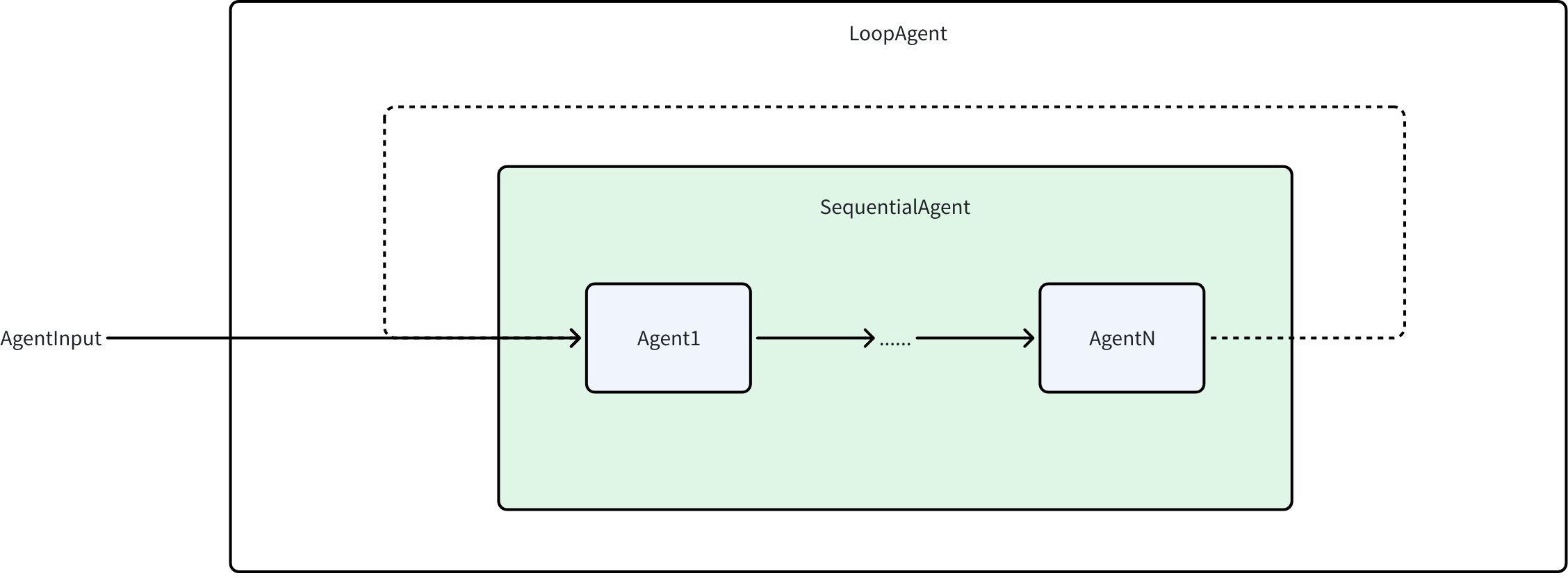
Agent 产生 ExitAction Event 时退出 LoopAgent,也可以配置 MaxIteration 来控制最大循环次数。通过 adk.NewLoopAgent 创建:
adk.NewLoopAgent(ctx, &adk.LoopAgentConfig{
Name: "name",
Description: "description",
SubAgents: []adk.Agent{a1,a2},
MaxIterations: 3,
})
ParallelAgent
ParallelAgent 会并发运行若干 Agent:
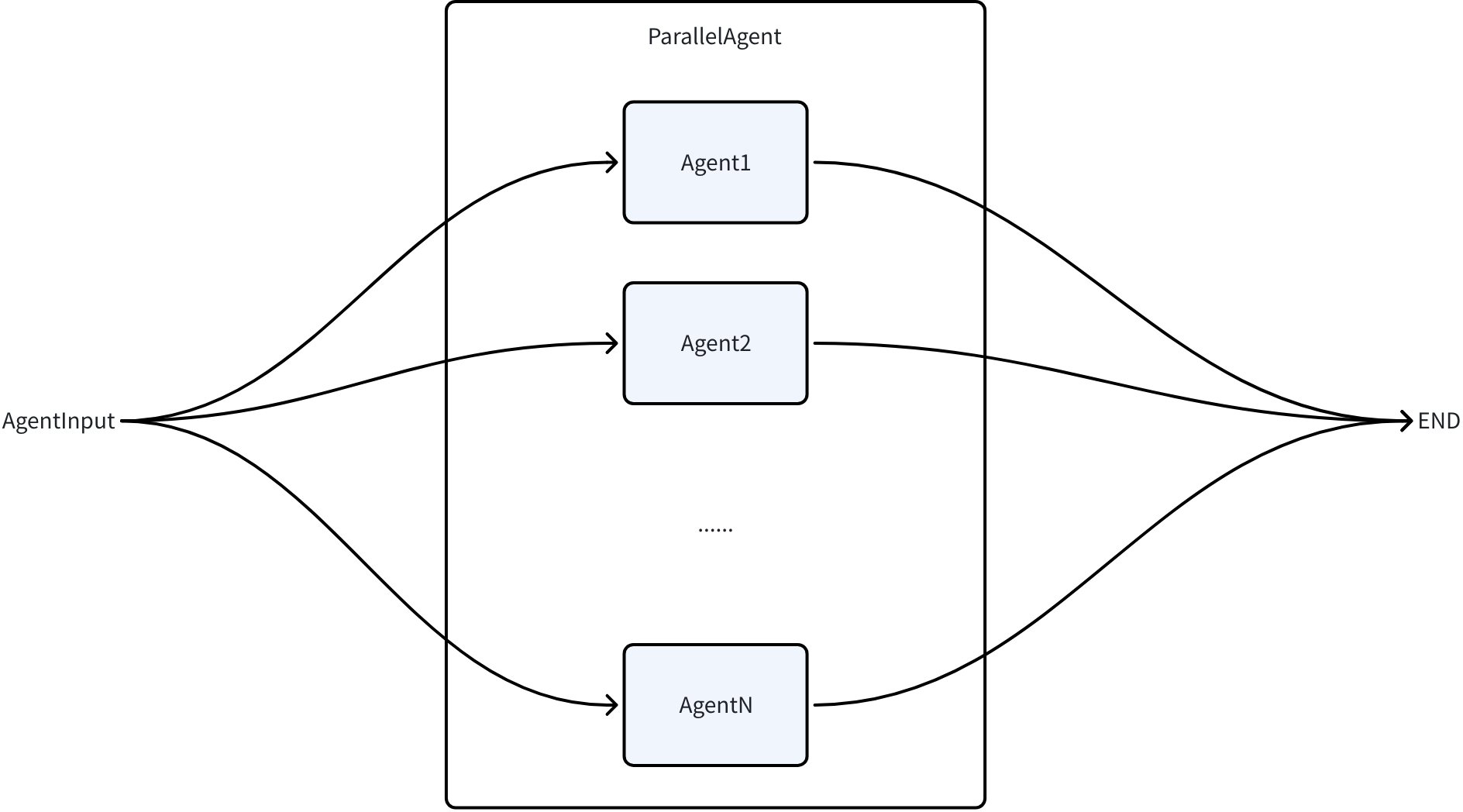
通过 adk.NewParallelAgent 创建:
adk.NewParallelAgent(ctx, &adk.ParallelAgentConfig{
Name: "name",
Description: "desc",
SubAgents: []adk.Agent{a1,a2},
})