Eino Dev Visual Debugging Guide
Overview
💡 Use this plugin to visually debug orchestration artifacts built with Eino (Graph, Chain):
- Visual rendering of orchestration
- Start from any operable node and debug with mock input
Quick Start
Download eino-examples
Repo: https://github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples
git clone https://github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples.git
# or
git clone git@github.com:cloudwego/eino-examples.git
Install Dependencies
In the project directory, run the following in order:
go get github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/devops@latest
go mod tidy
Run the Demo
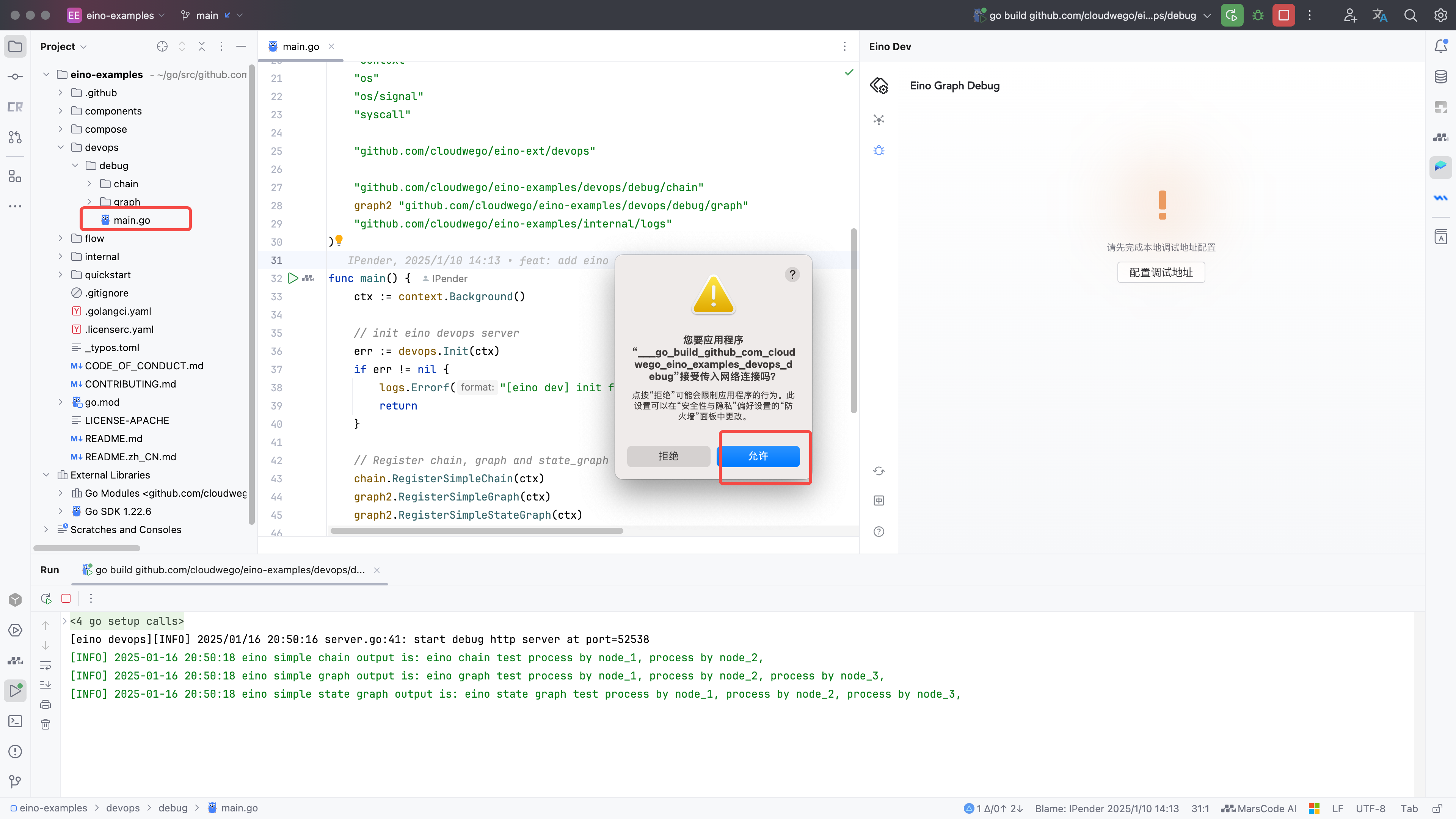
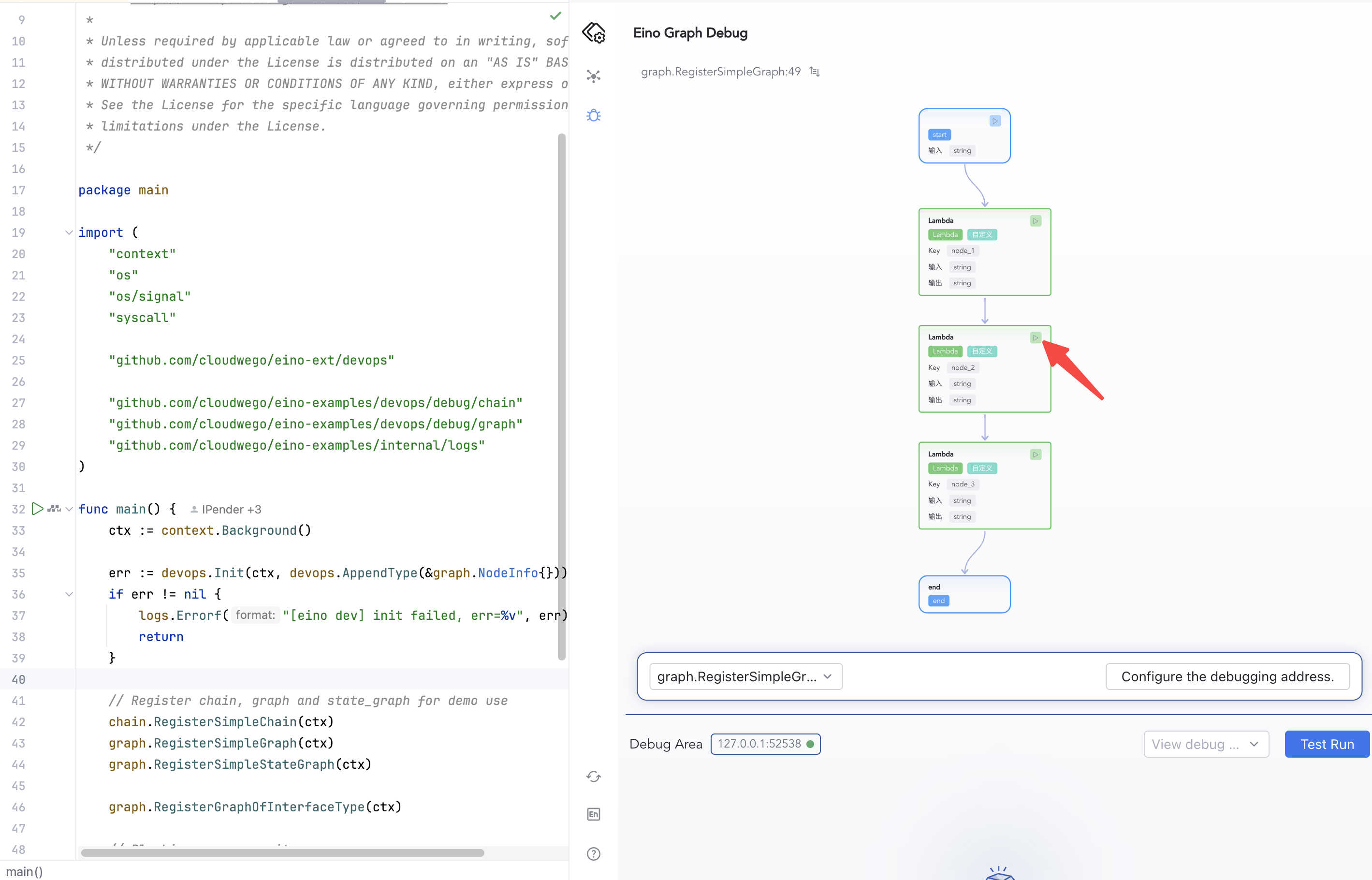
Open eino-examples/devops/debug/main.go and run main.go. The plugin launches a local HTTP service to connect to your process; allow network access if prompted.
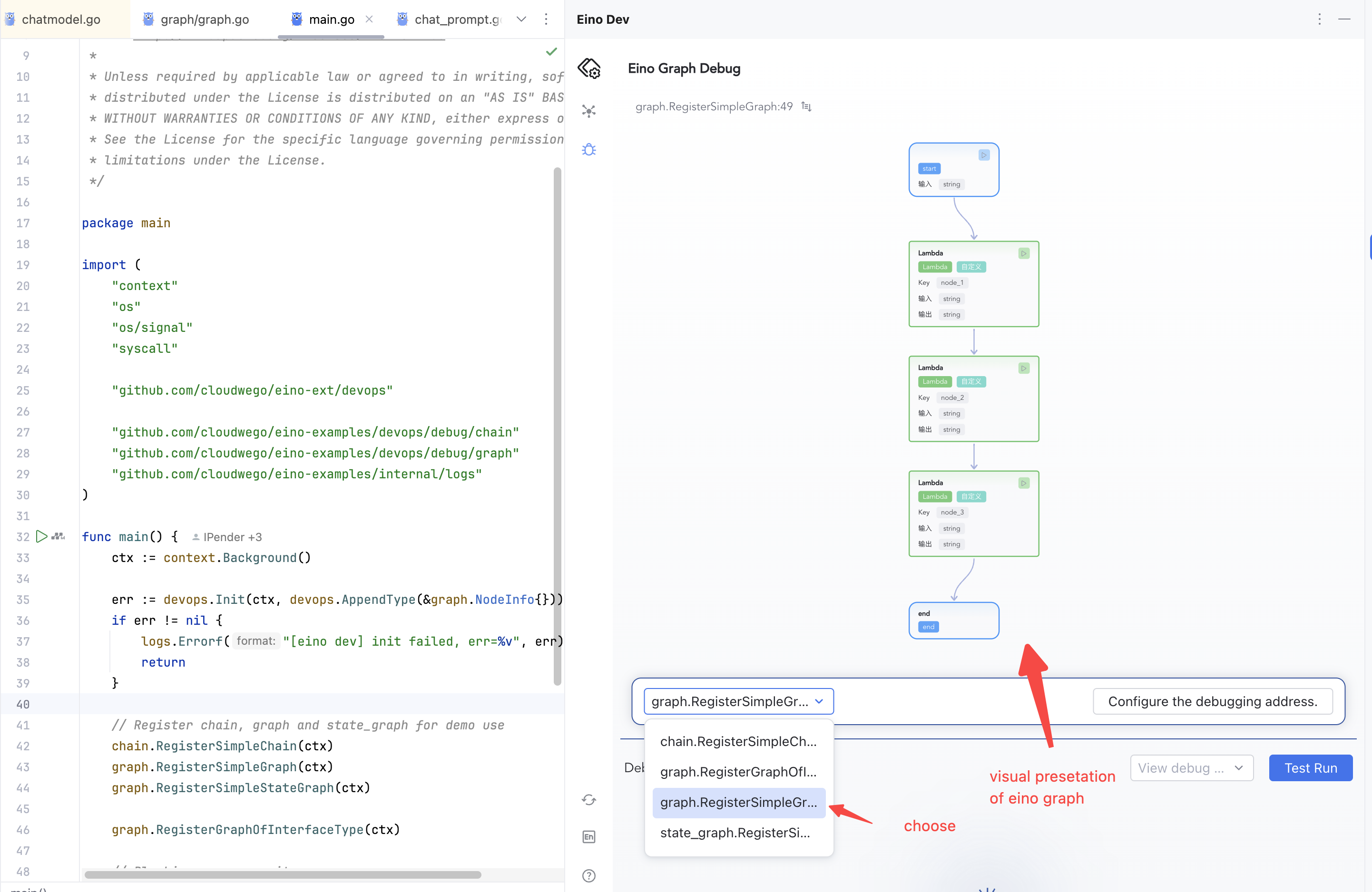
Configure Debug Address
1) Click the debug feature entry on the left or center to open configuration
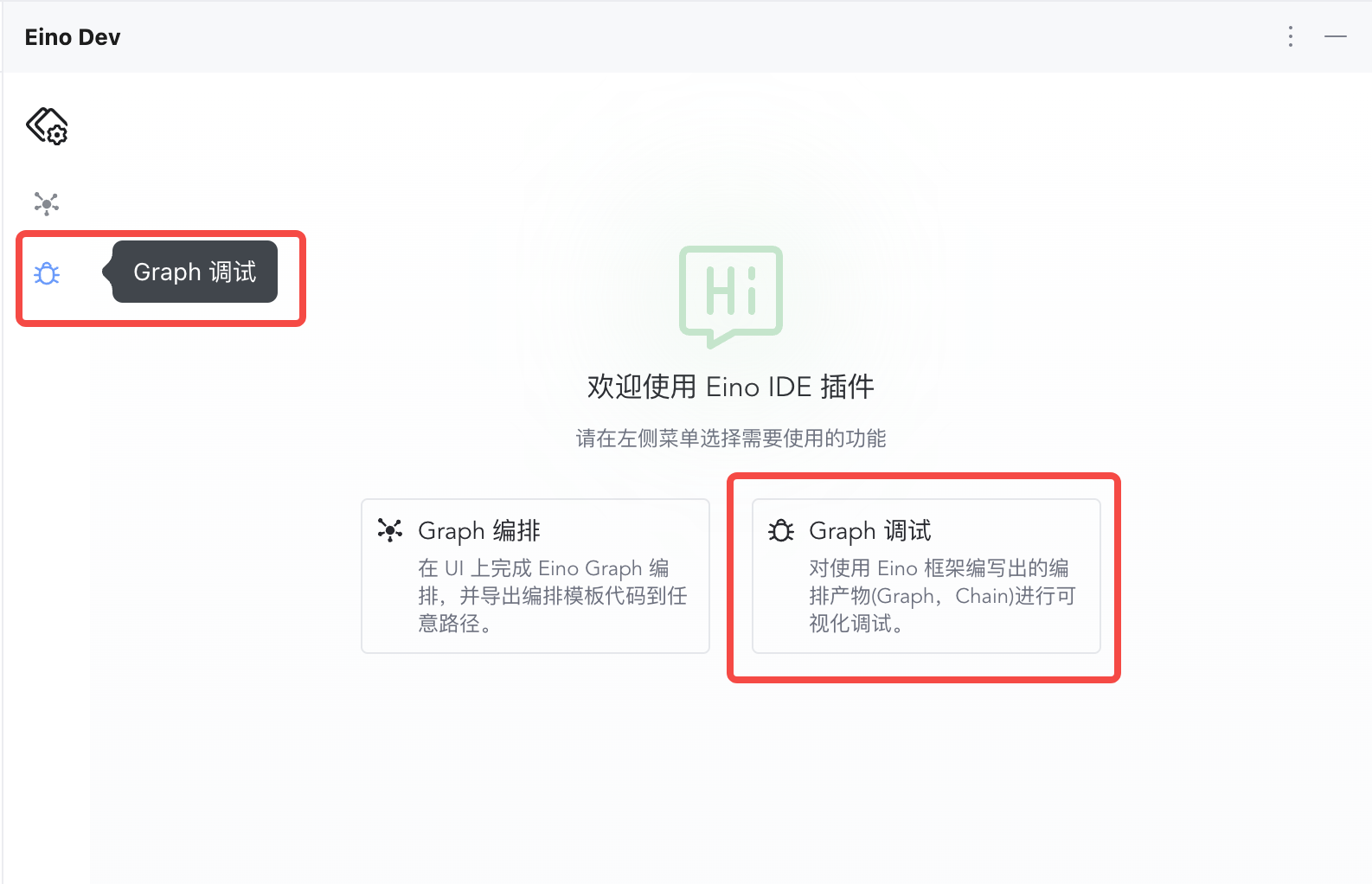 | 2) Click “Configure Address”
 |
3) Enter 127.0.0.1:52538
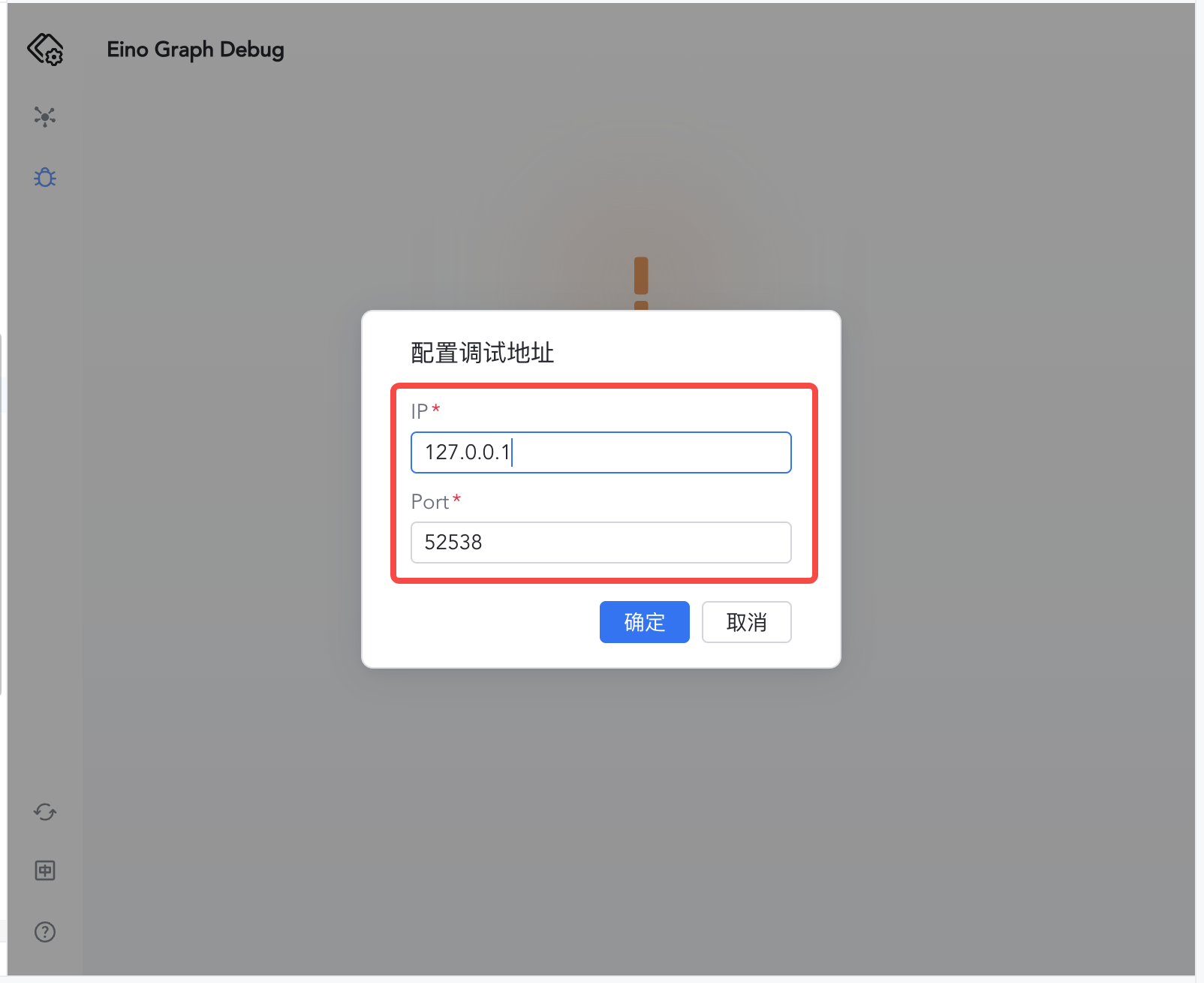 | 4) Confirm to enter the debug view, then select the Graph to debug
 |
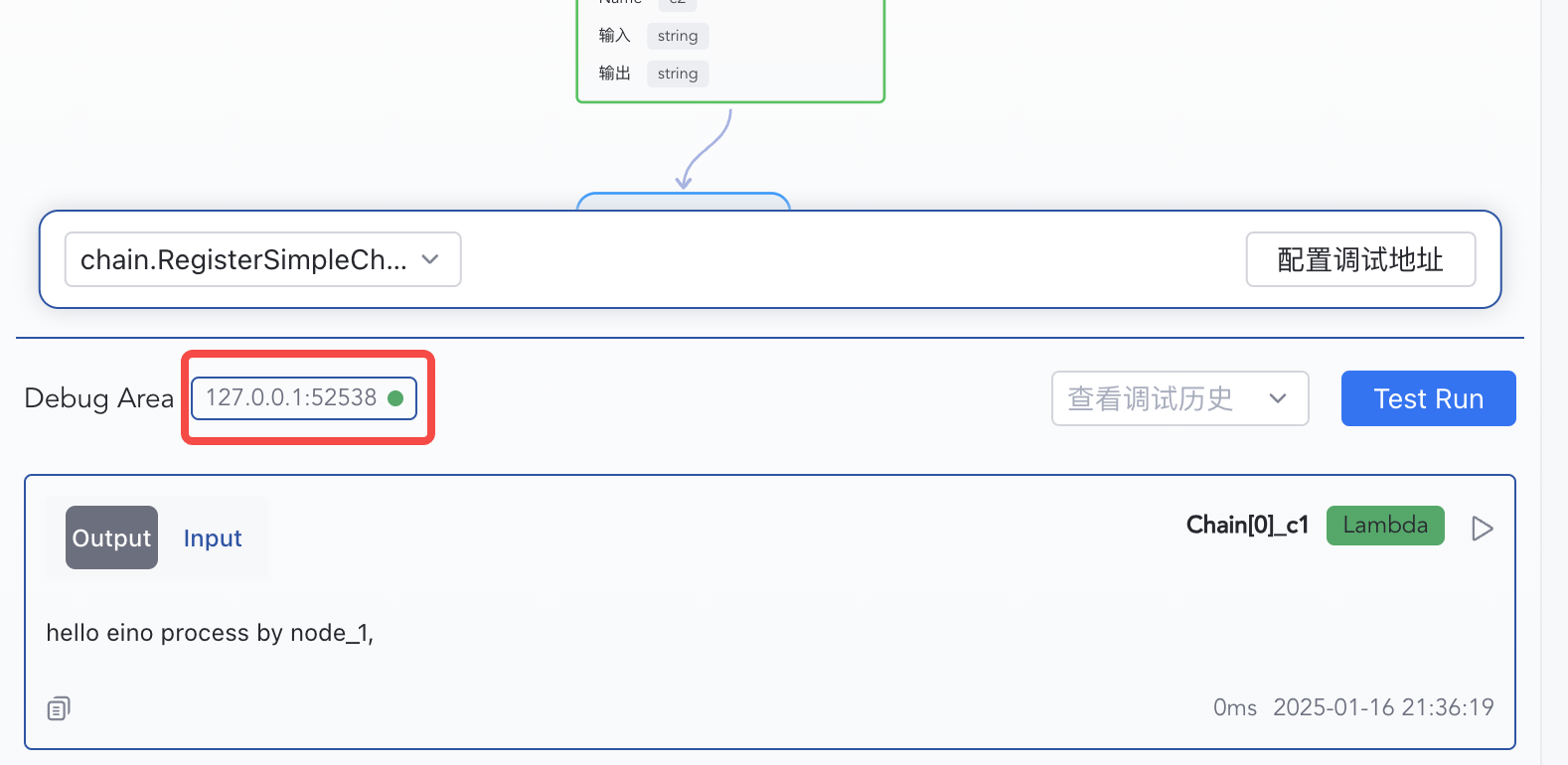
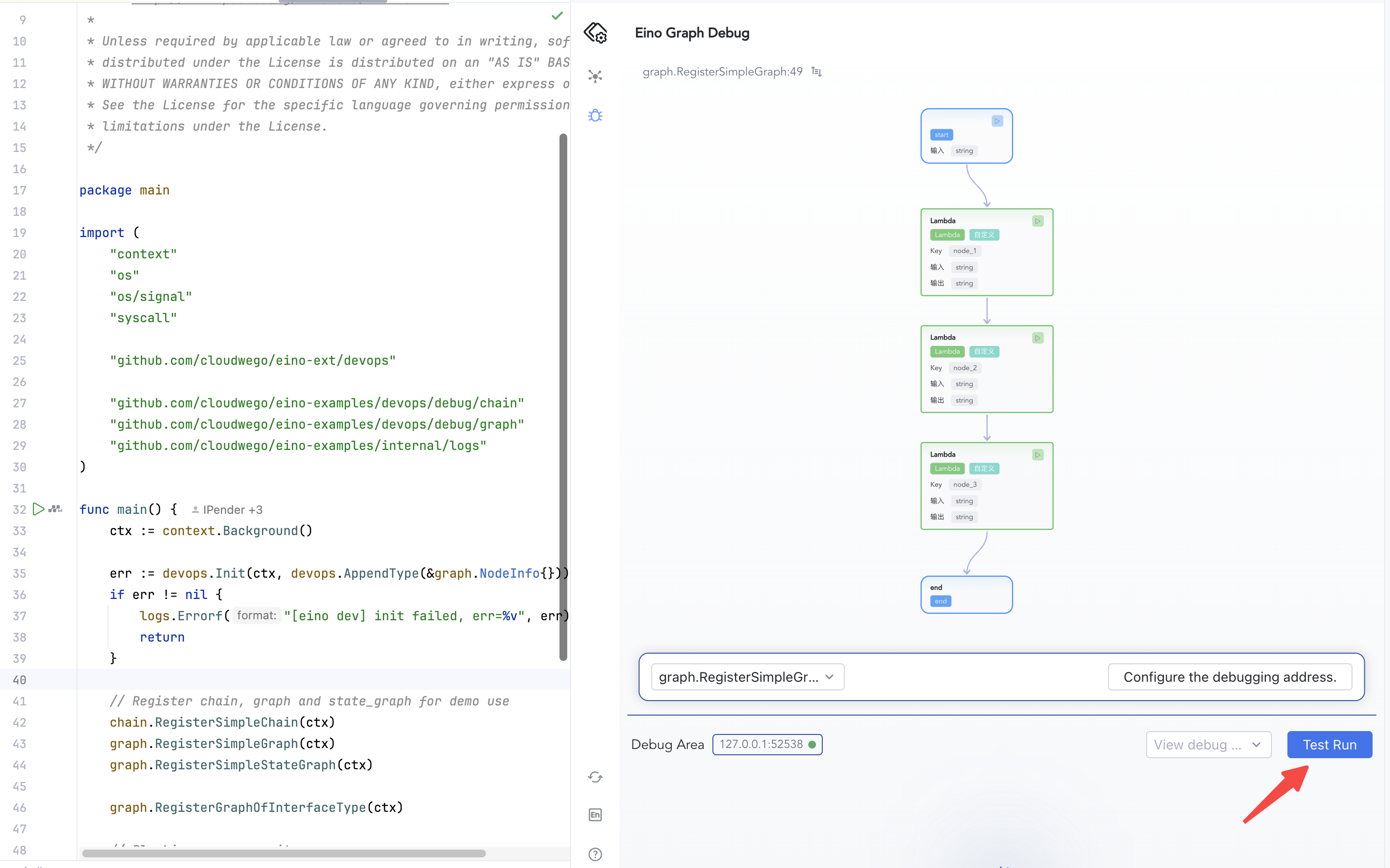
Start Debugging
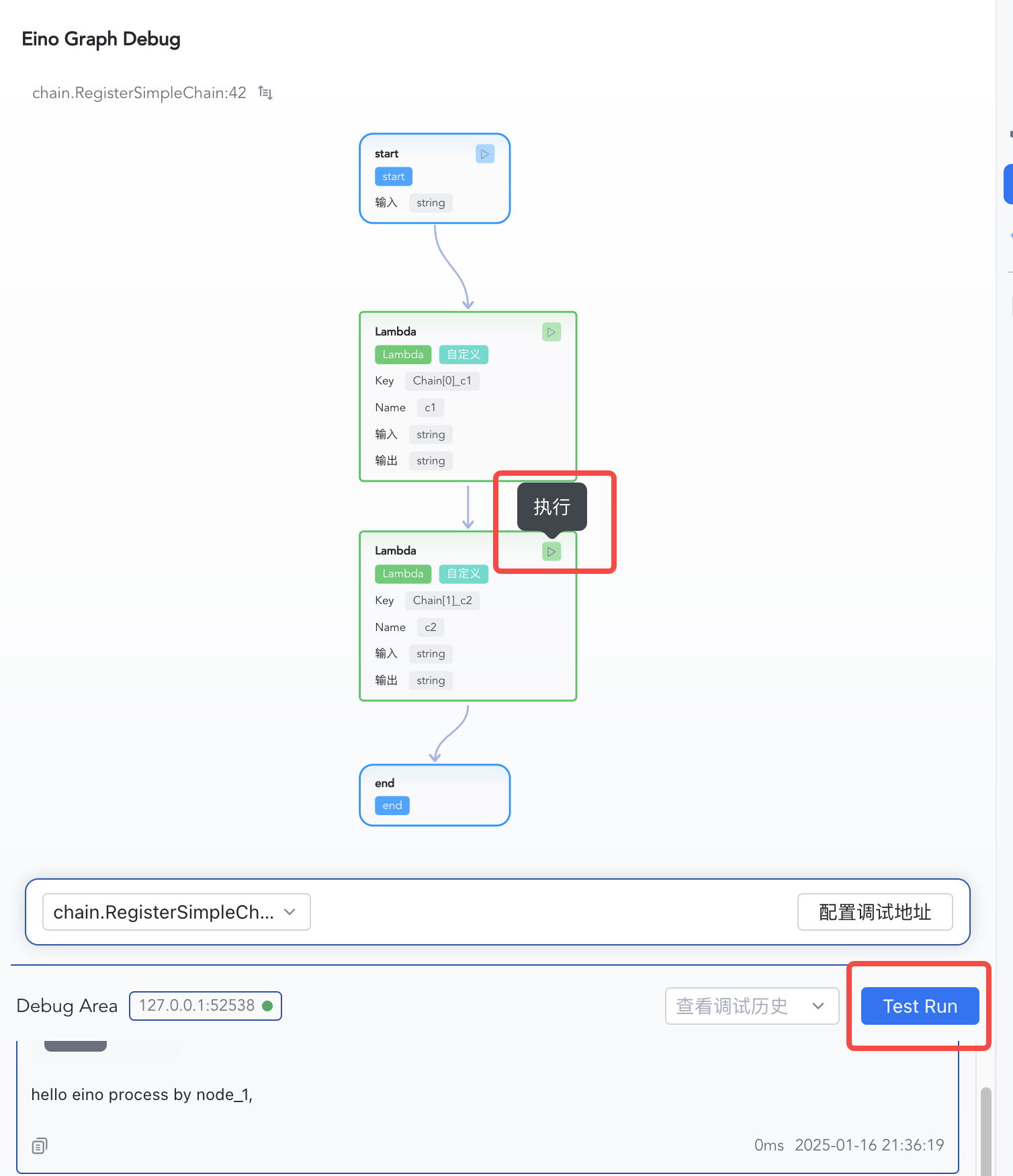
1) Click “Test Run” to start from START
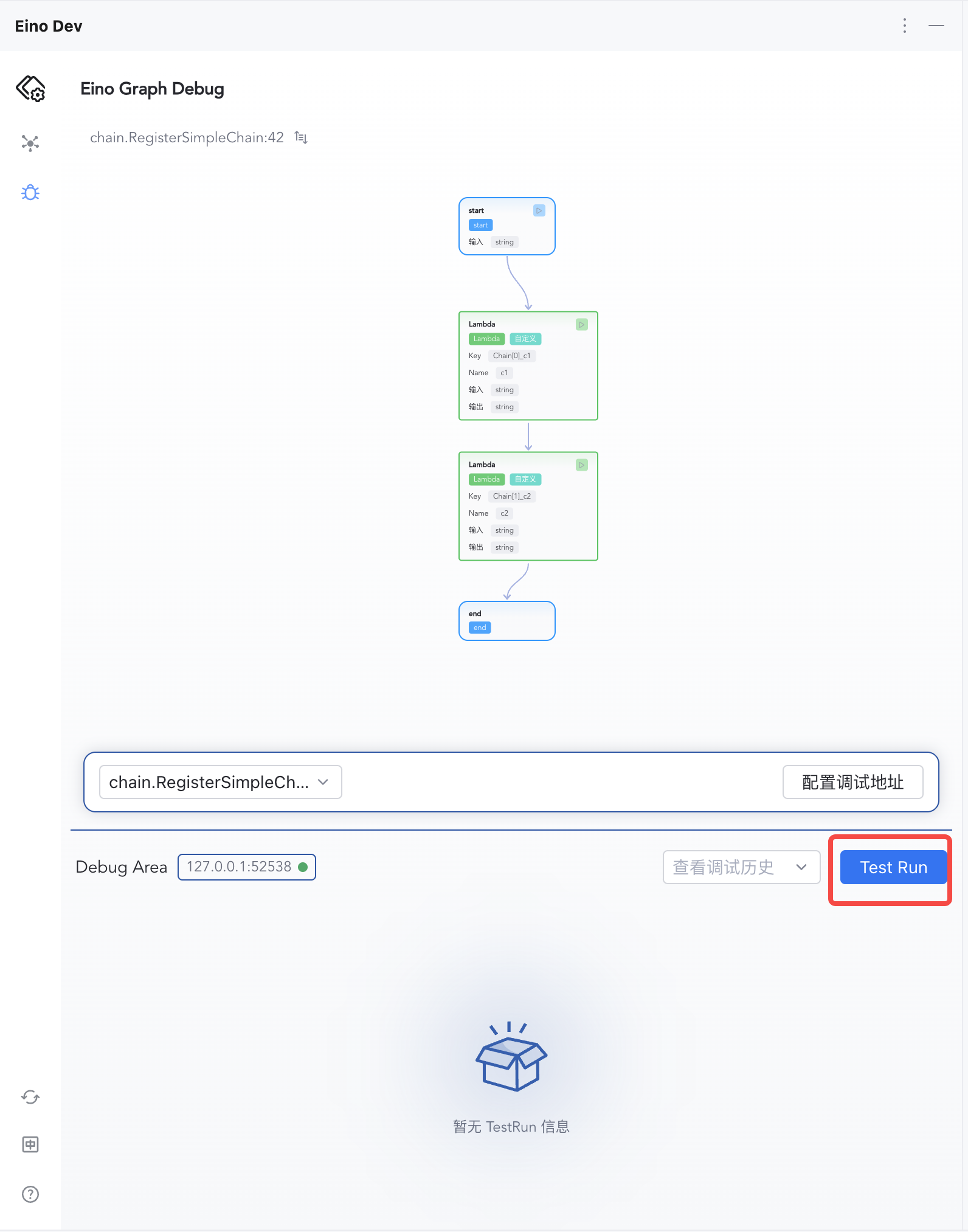 | 2) Enter "hello eino" and confirm
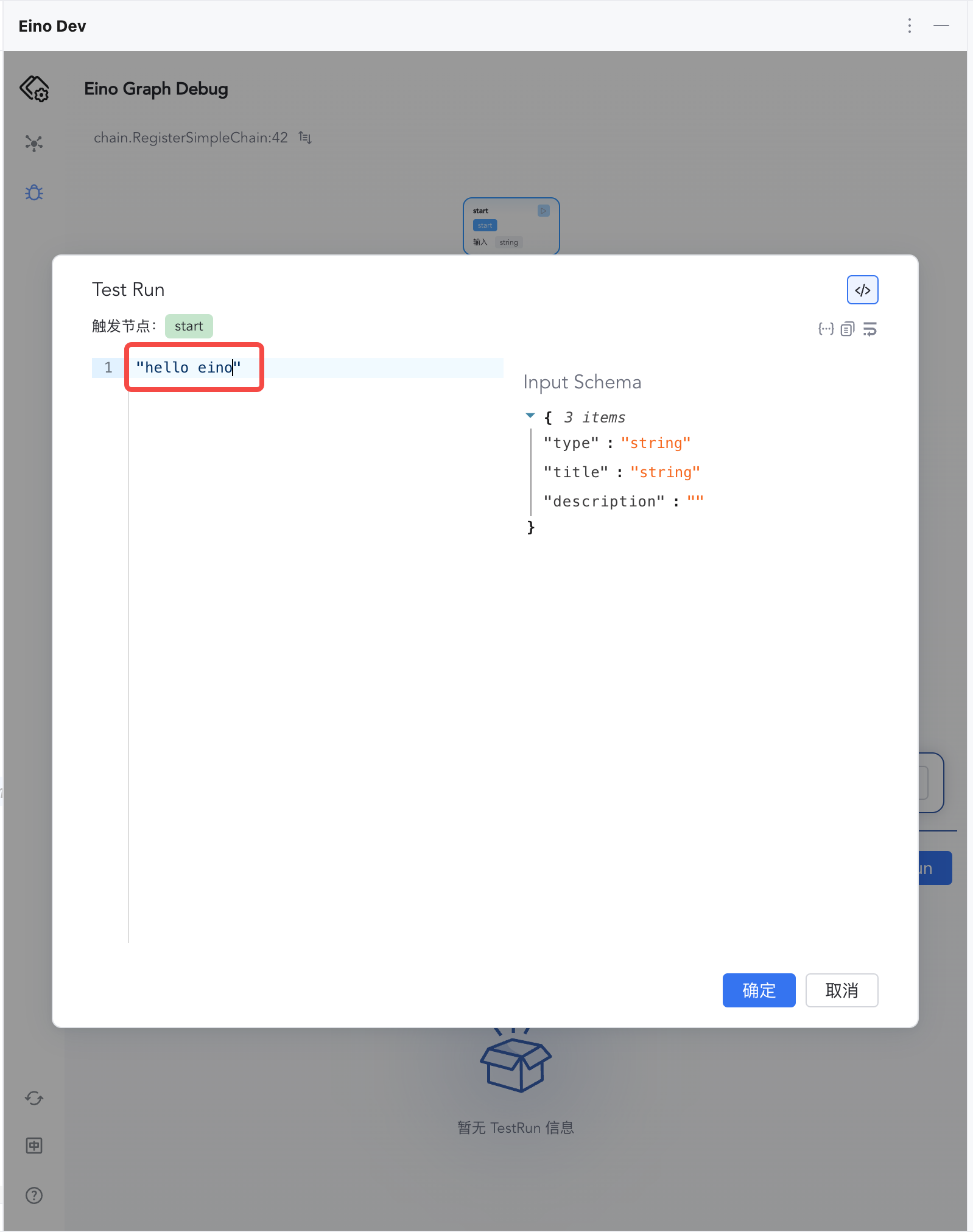 |
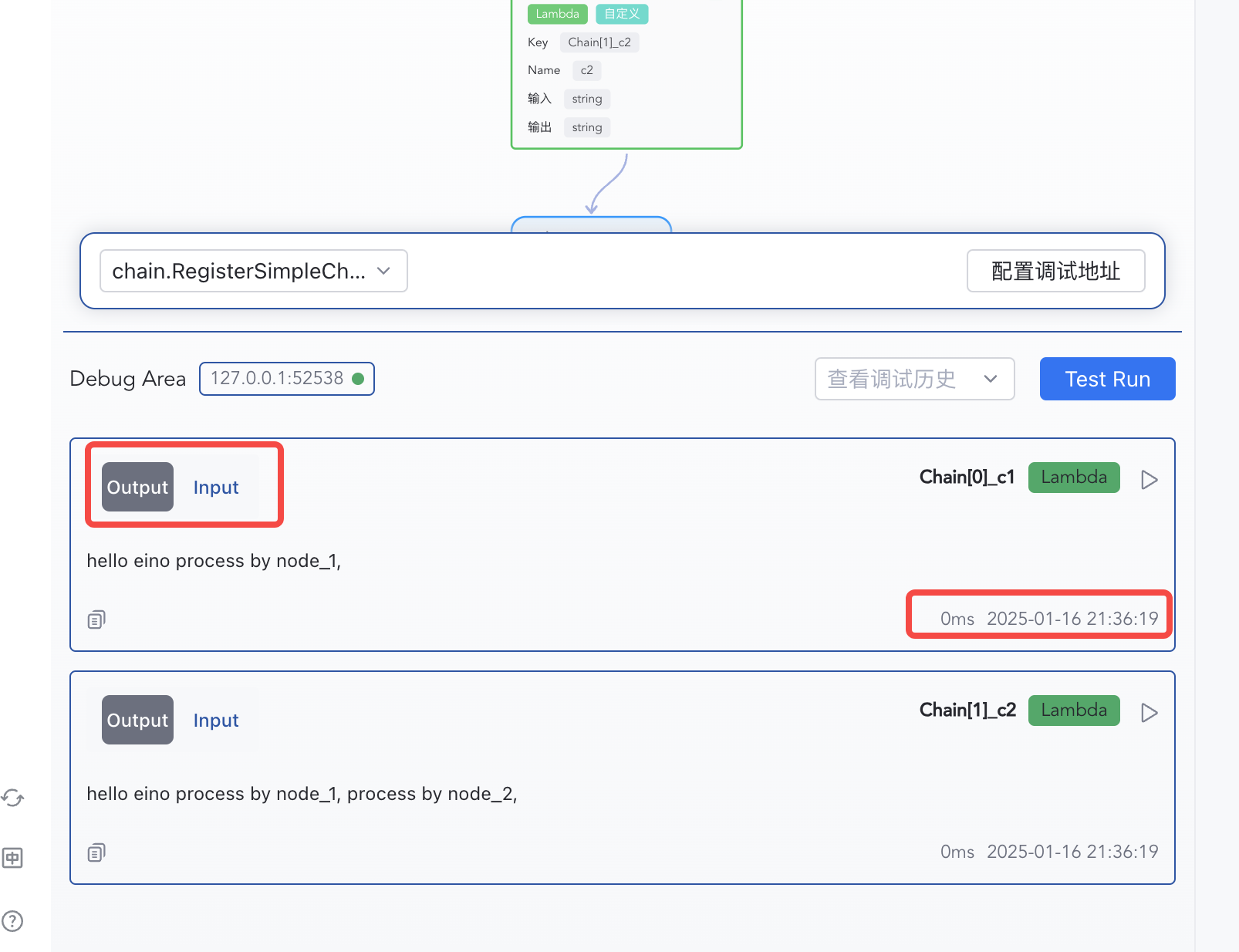
| 3) Inspect per-node inputs/outputs | 4) Switch Input/Output views |
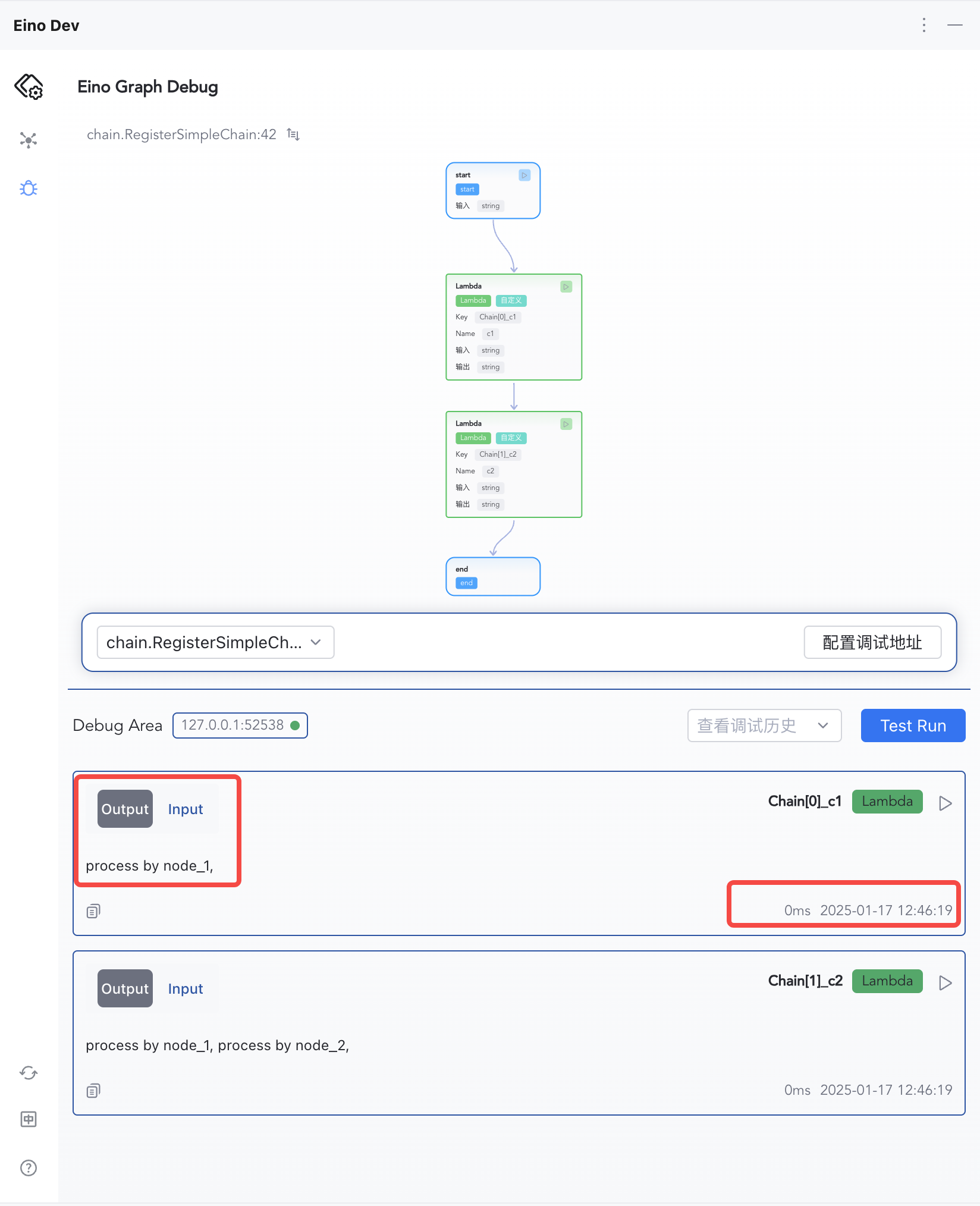 | 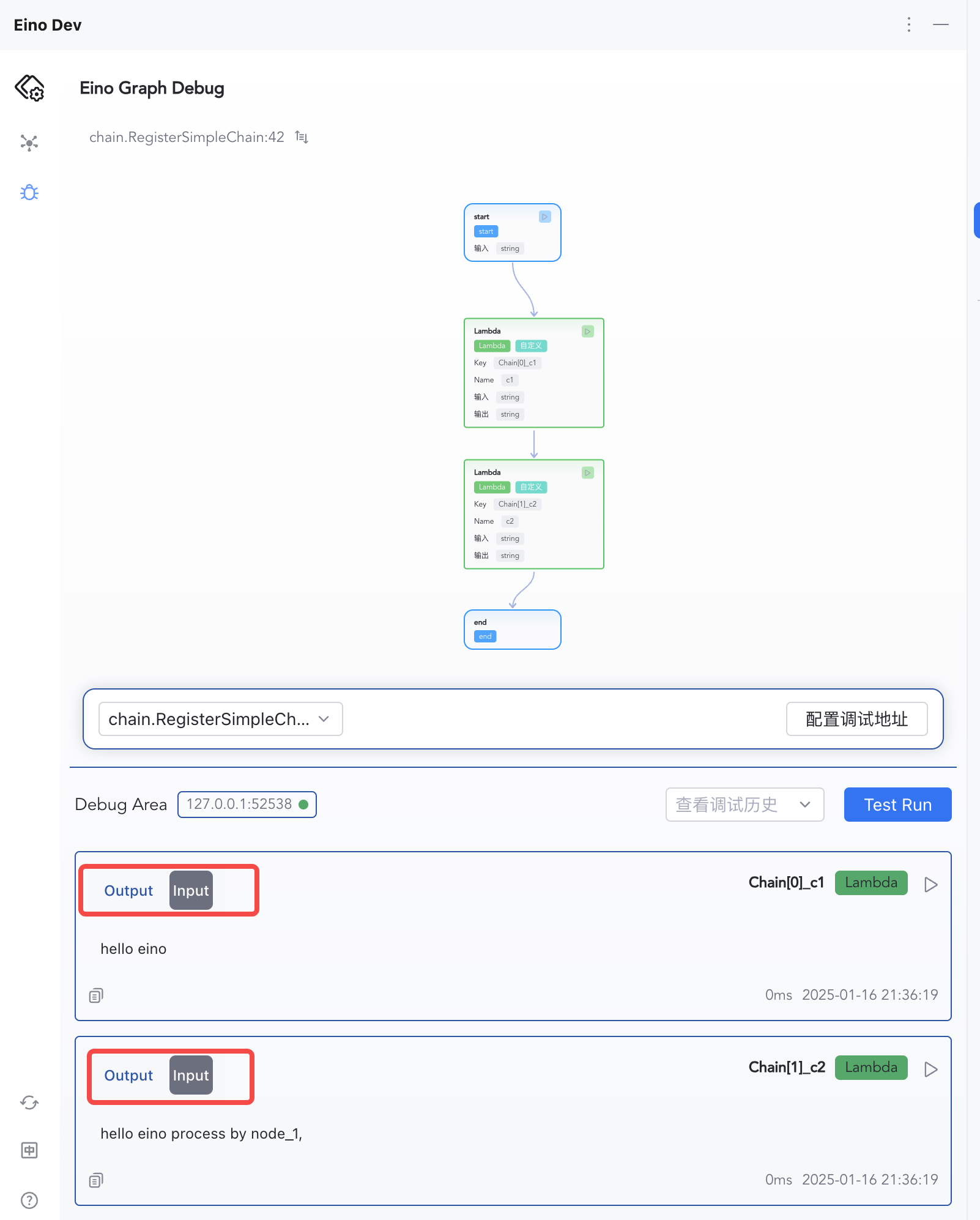 |
Feature Overview
Local or Remote Debugging
Configure IP:Port to connect to the target process, whether local or remote.
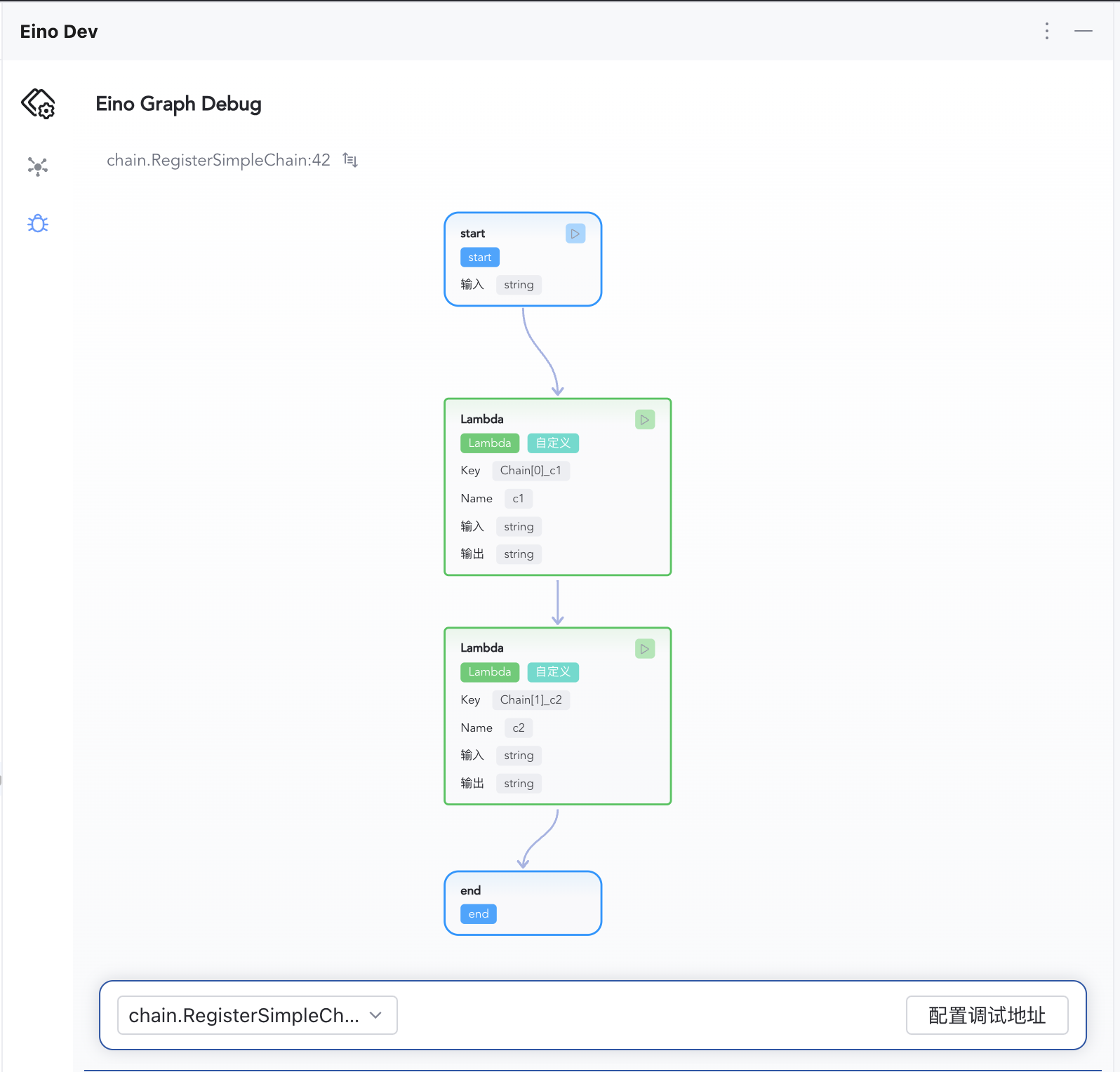
Orchestration Visualization
Supports Graph and Chain topology visualization.
Start from Any Node
Inspect Node Results
Each node’s input, output, and execution time are shown in order.
Debugging from Scratch
Orchestrate with Eino
The plugin supports debugging Graph and Chain artifacts. Example registration:
func RegisterSimpleGraph(ctx context.Context) {
g := compose.NewGraph[string, string]()
_ = g.AddLambdaNode("node_1", compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (output string, err error) {
return input + " process by node_1,", nil
}))
_ = g.AddLambdaNode("node_2", compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (output string, err error) {
return input + " process by node_2,", nil
}))
_ = g.AddLambdaNode("node_3", compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (output string, err error) {
return input + " process by node_3,", nil
}))
_ = g.AddEdge(compose.START, "node_1")
_ = g.AddEdge("node_1", "node_2")
_ = g.AddEdge("node_2", "node_3")
_ = g.AddEdge("node_3", compose.END)
_, err := g.Compile(ctx)
if err != nil {
logs.Errorf("compile graph failed, err=%v", err)
return
}
}
Install Dependencies
go get github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/devops@latest
go mod tidy
Initialize Debugging
Because debugging starts an HTTP service in your main process to interact with the local plugin, you must call Init() from github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/devops to start the debug service.
💡 Notes
- Ensure the target orchestration has run
Compile()at least once.devops.Init()must run before callingCompile().- Make sure the main process stays alive after
devops.Init().
// 1. Initialize debug service
err := devops.Init(ctx)
if err != nil {
logs.Errorf("[eino dev] init failed, err=%v", err)
return
}
// 2. Compile the target orchestration artifact to debug
RegisterSimpleGraph(ctx)
Run Your Process
Run your process locally or remotely, and ensure the main process does not exit.
In github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples/devops/debug/main.go, main() looks like:
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Init eino devops server
err := devops.Init(ctx)
if err != nil {
logs.Errorf("[eino dev] init failed, err=%v", err)
return
}
// Register chain, graph and state_graph for demo use
chain.RegisterSimpleChain(ctx)
graph.RegisterSimpleGraph(ctx)
graph.RegisterSimpleStateGraph(ctx)
// Blocking process exits
sigs := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(sigs, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
<-sigs
// Exit
logs.Infof("[eino dev] shutting down\n")
}
Configure Address
- IP:
127.0.0.1for local; remote server IP for remote (IPv4/IPv6). - Port: default
52538, configurable viaWithDevServerPort.
Allow network prompts locally; ensure remote ports are reachable. Once connected, the status indicator turns green.
Select an Artifact
Ensure your target orchestration has been compiled at least once. Multiple Compile() runs register multiple artifacts; you’ll see them in the selection list.
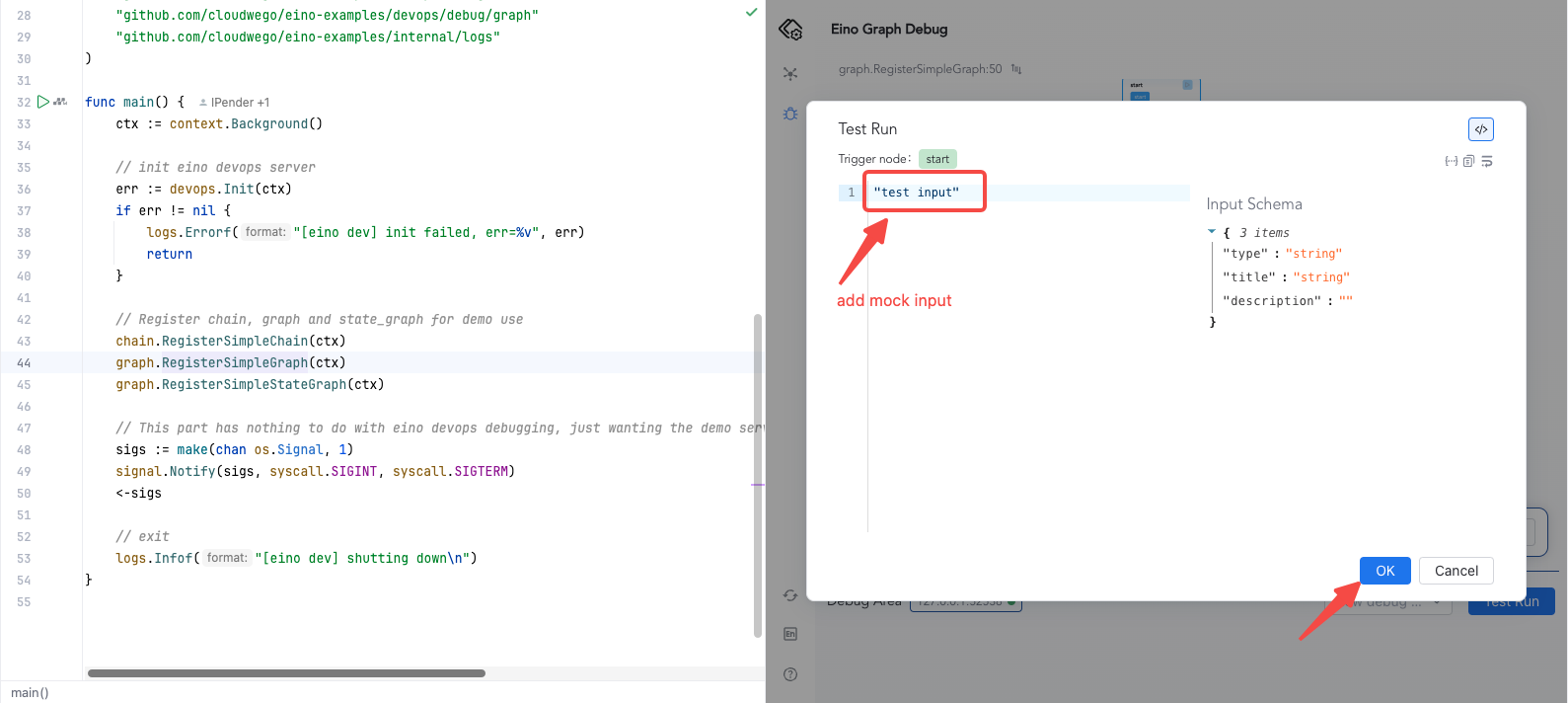
Start Debugging
- From START: click “Test Run”, enter mock input (complex types are inferred), and confirm.
- From a specific node: click the run button on that node.
Advanced
Specify Implementation Type for Interface Fields
Interface-typed fields render as {} by default. Type a space inside {} to select an implementation type. The plugin uses a special JSON structure:
{
"_value": {}, // JSON value of the concrete type
"_eino_go_type": "*model.MyConcreteType" // Go type name
}
💡 Common interface types like
string,schema.Messageare built-in. To register custom types, usedevops.AppendTypeduringInit().
- Suppose you have orchestration code where the graph input is
any, andnode_1takes*NodeInfo:
type NodeInfo struct {
Message string
}
func RegisterGraphOfInterfaceType(ctx context.Context) {
// Define a graph that input parameter is any.
g := compose.NewGraph[any, string]()
_ = g.AddLambdaNode("node_1", compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input *NodeInfo) (output string, err error) {
if input == nil {
return "", nil
}
return input.Message + " process by node_1,", nil
}))
_ = g.AddLambdaNode("node_2", compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (output string, err error) {
return input + " process by node_2,", nil
}))
_ = g.AddLambdaNode("node_3", compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (output string, err error) {
return input + " process by node_3,", nil
}))
_ = g.AddEdge(compose._START_, "node_1")
_ = g.AddEdge("node_1", "node_2")
_ = g.AddEdge("node_2", "node_3")
_ = g.AddEdge("node_3", compose._END_)
r, err := g.Compile(ctx)
if err != nil {
logs.Errorf("compile graph failed, err=%v", err)
return
}
}
- Before debugging, register the custom
*NodeInfotype withAppendTypeatInit():
err := devops.Init(ctx, devops.AppendType(&graph.NodeInfo{}))
- During Test Run, interface fields show
{}by default. Type a space inside{}to view all built-in and custom types, select the concrete implementation, then fill_value.
Debugging map[string]any
If a node input is map[string]any:
func RegisterAnyInputGraph(ctx context.Context) {
g := compose.NewGraph[map[string]any, string]()
_ = g.AddLambdaNode("node_1", compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input map[string]any) (output string, err error) {
for k, v := range input {
switch v.(type) {
case string:
output += k + ":" + v.(string) + ","
case int:
output += k + ":" + fmt.Sprintf("%d", v.(int))
default:
return "", fmt.Errorf("unsupported type: %T", v)
}
}
return output, nil
}))
_ = g.AddLambdaNode("node_2", compose.InvokableLambda(func(ctx context.Context, input string) (output string, err error) {
return input + " process by node_2,", nil
}))
_ = g.AddEdge(compose.START, "node_1")
_ = g.AddEdge("node_1", "node_2")
_ = g.AddEdge("node_2", compose.END)
r, err := g.Compile(ctx)
if err != nil {
logs.Errorf("compile graph failed, err=%v", err)
return
}
message, err := r.Invoke(ctx, map[string]any{"name": "bob", "score": 100})
if err != nil {
logs.Errorf("invoke graph failed, err=%v", err)
return
}
logs.Infof("eino any input graph output is: %v", message)
}
During debugging, in the Test Run JSON input box, use the following format to specify concrete types for values:
{
"name": {
"_value": "alice",
"_eino_go_type": "string"
},
"score": {
"_value": "99",
"_eino_go_type": "int"
}
}